5 Technology Trends That Will Dominate In 2023

As the digital transformation landscape continues to evolve and new technologies emerge, it's important that we don't lose sight of the core drivers of digital transformation: sustainability, data volumes, and compute and network speeds.
The last two years have taught us that truly transformative change isn't as difficult to implement as might once have been thought. If the motivation is there, we will undoubtedly continue to harness this newfound openness to flexibility and innovative thinking.
In 2023, it’s likely that the biggest technology trends will combine to produce a world unlike anything we’ve ever seen. Quantum computing, neural interfaces, and nanotechnology are just a few of the tools in development that will combine to create a future unlike any we’ve ever imagined.
1. Digitization, datafication and virtualization
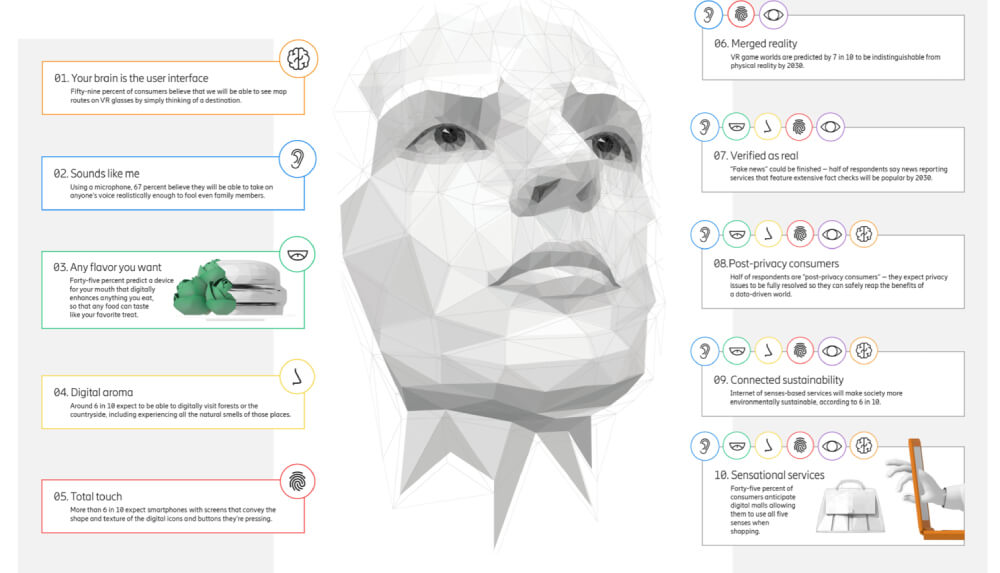
As digitization continues to increase, metaverses will become increasingly realistic models of the real world. The result will be immersive, convincing experiences that are more valuable because they are not limited by physical boundaries. While many people have had somewhat immersive VR experiences through headsets, a range of new devices coming to the market will greatly improve the experience and offer tactile feedback and even smells.
In 2021, Swedish telecommunication company Ericsson predicted that by 2030 virtual experiences and environments will be indistinguishable from reality. A new sci-fi movie in 2023 might bring us a step closer to entering that universe for ourselves.
Consumers predict that by 2025 we will be wearing lightweight, fashionable augmented reality glasses. These glasses will allow us to see and manipulate digital objects, instantly translate languages and allow us to experience smell, taste and temperature digitally.
2. Artificial Intelligence
The use of artificial intelligence has become ubiquitous in the tools we use to carry out everyday work. These include voice assistants, language translation, tools for extracting structured data from images and notes, and robotic process automation that has enabled workloads to be lightened in administrative, logistical, accounting, and human resources departments.
On a broader scale, we are seeing a convergence of artificial intelligence (AI), the internet of things (IoT), and faster networks like 5G. These technologies are enabling capabilities like augmented reality that did not exist just a few years ago. This convergence will affect society in a way that is much more than the sum of its parts.
3. Transparency and accountability
Many people are afraid of AI because they can't see inside it. This stems from the technology's complexity rather than any sort of malevolent scheme to limit our understanding, however, the effect is the same: Our fear makes us uneasy around the idea of AI being in control of hiring and firing, for example.
National governments have also taken steps to address the need for a regulatory framework. For example, the European Union (EU) proposed the Artificial Intelligence Act in 2017, which prohibits authorities from using AI to create social scoring systems and requires that companies demonstrate their systems will not cause physical or psychological harm before they can be offered for sale. The act also prohibits authorities from using facial recognition tools in public places. Some privacy advocates claim that this doesn’t go far enough because it doesn’t contain any stipulation that people should be informed when they become subjects of AI-driven decision-making processes. This balancing act is likely to become an increasingly prominent subject of discussion during 2023 as more people become aware of the potential positive and negative effects on society that AI and other technology trends will have.
4. Cloud solution and the no-code revolution
In recent years, cloud services have been increasingly used by both small and large businesses to try out new ideas at a low cost and with minimal risk. Hybrid solutions are also growing in popularity; they allow companies to take advantage of public cloud services while keeping certain types of data on their own servers.

As natural language processing technology improves and converges with cloud computing, coding will increasingly become optional for innovators. OpenAI recently unveiled Codex, a program that writes code from natural human language input (e.g., "I want to print the first 100 numbers in the Fibonacci sequence"). As this type of technology becomes more mature, it will enable ideas that today would be impossible because of barriers associated with resources or technical skills.
5.Sustainable energy solutions
The International Energy Agency (IEA) estimates that renewable energy generation and consumption has increased by 40% during 2020 compared to the previous year and forecasts this growth will continue throughout 2023. Overall, the cost of generating renewable energy from various sources, including onshore and offshore wind, solar and tidal, fell by between seven and 16%. This will be a huge help for countries and businesses trying to hit emissions targets, such as becoming carbon neutral or even carbon negative.
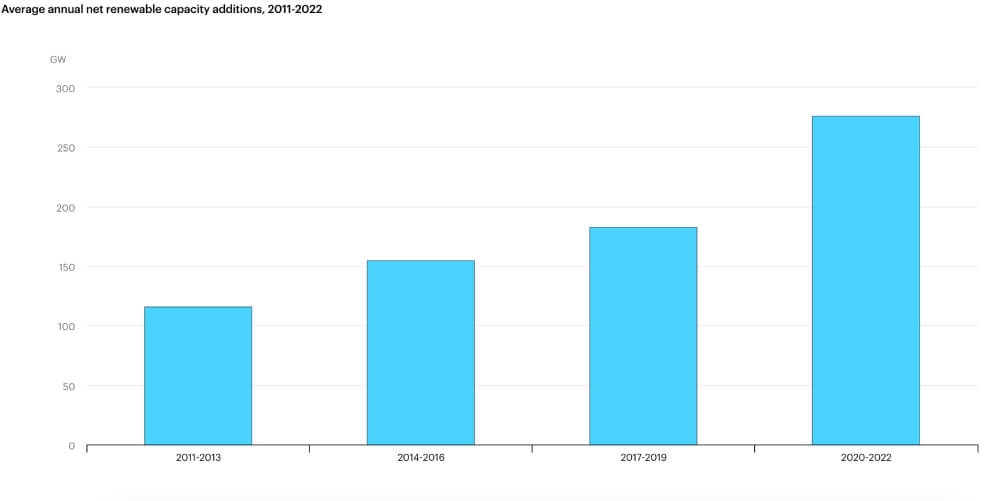
Fusion energy – which replicates the process used to create energy in the sun – is expected to come online in 2023, according to Helion Energy. Practical applications of this new technology are also expected in the field of “green hydrogen” energy. Unlike the established processes for creating energy from hydrogen, which involve using large amounts of fossil fuel energy to create electrolysis and separate hydrogen and oxygen without emitting carbon, this involves using renewable energy, dampening the overall environmental impact.
Concluding, the future is filled with many uncertainties. But one thing is certain: even though technology will change, we will always be making a difference in the lives of everyone.
More Insights
Outsourcing can be a great way to bring in new skills, but it’s also a way to make sure that your business is protected, both financially and legally.
The Minimum Viable Product Theory was first introduced in a blog post by Frank Robinson in order to define the nature of a "product" in the context of increasing returns and reducing risks.
As the digital transformation landscape continues to evolve and new technologies emerge, it's important that we don't lose sight of the core drivers of digital transformation: sustainability, data volumes, and compute and network speeds.
Follow the latest technology and thought leadership by subscribing to Atomate newsletters.
Dive into cutting-edge tech trends and visionary insights, curated monthly for forward-thinkers like you.
